GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE DEPARTMENT
Patient services, Clinical and Laboratory Applications
The Department provides outpatient and clinical services related to immunodeficiency and allergic diseases. At the same time, it provides consultation services to other departments that perform stem cell and organ transplantation (Haematology, Oncology, Nephrology, Surgery) within the hospital.
In our department, adult patients who are thought to be immunodeficient are diagnosed using advanced technology devices and systems (flow cytometry, Luminex) in the tissue typing laboratory and treated with current methods. Our hospital has the most experienced physicians and allied health professionals in this field in Turkey.
In Başkent University, one of the most emphasized and developed fields is Tissue and Organ Transplantation Immunology. The tissue typing laboratory had been established to serve this purpose. The tests that determine whether there is tissue compatibility between recipient and donor candidates are performed in this laboratory. In addition, advanced information about the possibility of organ rejection are given after the evaluation of the test results by clinical immunologist. Thus, the chance of transplantation success is being increased by minimizing the error rate.
DISEASES RELATED TO DEPARTMENT
IMMUNODEFICIENCIES
The immune system consists of tissues and organs that defend the body against microbes. Immunity is the task of the cells called as leukocytes, which are the constituents of this system. These cells fight against microbes and produce some toxic substances against them. Therefore, the lack of leukocytes in the number or function causes diseases called as immunodeficiencies. Many immunodeficiencies diagnosed in childhood occur due to hereditary causes. In adults, the effect of environmental factors (exposure to chemicals or radiation, air or environmental pollution, etc.) is more pronounced. Recurrent infections are the most characteristic feature of these diseases. These are resistant to drug treatments and often requires long-term antibiotic use. The signs and symptoms of these diseases may be different especially in adulthood. Organ growth (liver, spleen, lymph gland) due to unknown cause, decrease in the number of blood cells and the occurrence of rheumatic or allergic complaints are some of them. Therefore, the patients often refer to different branch physicians instead of immunologists. On the other hand, the level of social awareness about these diseases is low. It is noteworthy that these diseases are also not well known among health workers. Therefore, the patients have delays in diagnosis and their treatment start at late period. The most negative aspect of this is the permanent dysfunction of affected organs due to recurrent infections. Because of these, early diagnosis and correct treatment are very important in terms of patient's life expectancy and quality.
Diagnosis of Immunodeficiencies
Immunodeficiencies are diagnosed by patient examination and some special laboratory tests. Blood tests are carried out in two stages. In the first stage, screening tests are performed and in the second stage more specific tests are performed. Thus, detailed analyses of abnormal findings detected in screening tests are performed. The tests in the first stage able to be performed in many routine laboratories. The specific tests can only be performed in advanced laboratories where advanced technology systems (Flow cytometry, Luminex) are used. In addition, it is necessary to have staff specialized in immunodeficiencies in order to interpret all these tests correctly.
Treatment
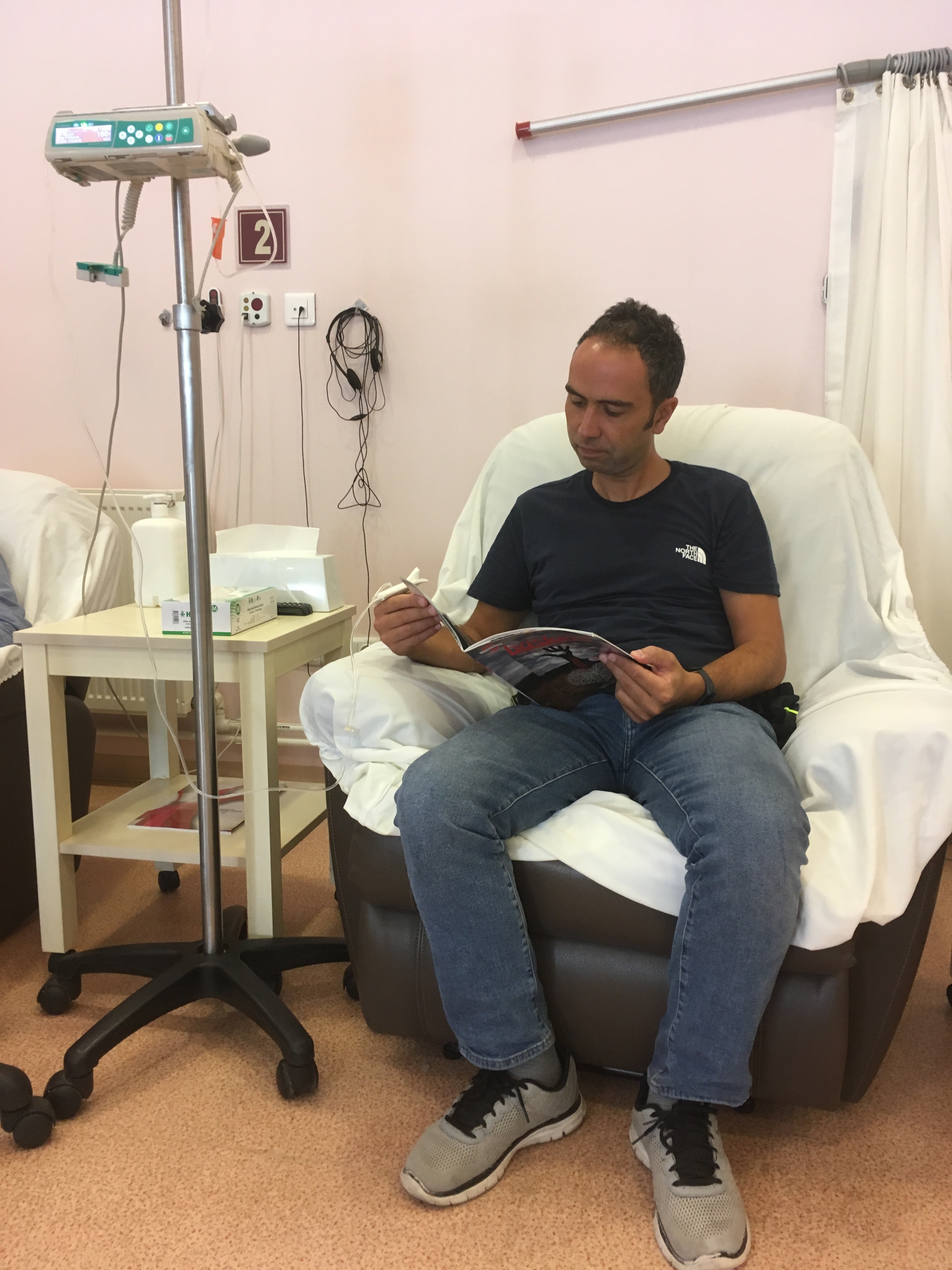
Some patients diagnosed in childhood can be treated fully by stem cell transplantation. However, this method of treatment is applied to the patients who are affected several different components of the immune system and have a severe form of diseases. The remaining children or adult patients are given treatments that support the immune response. The most important of these is antibody therapy administered by intravenous route every 3-4 weeks (Figure 1). This treatment (intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: IVIG) lasts between 2-4 hours according to the patient's tolerance and is performed under the supervision of a physician. Antibody therapy can be administered by subcutaneously (SCIG). However, this latter method has not yet become widespread. The aim of antibody treatment is to reduce the frequency and severity of infections, thus preventing future organ failure.
Figure 1. A patient receiving intravenous antibody therap
In immunodeficiencies, it is important for patients to visit their physicians regularly. They also need to pay attention to their diet and change their lifestyle appropriately. These are other factors that positively affect the course of the disease. Providing psychosocial support to patients with adaptation problems in school and work life is also important clinical practice that increases the effectiveness of medical treatments.
ALLERGIC DISEASES
These diseases are caused by substances called allergens that stimulate the immune system after entering the body and produce an exaggerated response in individuals with genetic predisposition (atopic). Allergy symptoms vary according to the affected tissue and organ: allergic rhinitis when the nose is affected, allergic conjunctivitis when the eye is affected, allergic asthma when the respiratory system is affected, and urticaria (hives, dabas) or eczema when the skin is affected. If more than one system is affected, a clinical picture is called anaphylactic shock which requires immediate intervention. In this life-threatening condition, low blood pressure and loss of consciousness, urticaria, respiratory distress and abdominal pain occur. Sometimes swelling in the throat obstructs the airways and results in death.
The main symptoms in patients with allergic rhinitis are successive sneezing, runny nose (such as water), postnasal drainage and itching. In some patients, conjunctivitis characterized by itching and itching in the eyes develop. Allergens are mostly mould and mites in the home but are pollens outside the home. Allergic rhinitis can progress to a more severe disease, asthma, when it is not diagnosed and treated early. Asthmatic patients have complaints of coughing, difficulty breathing and wheezing. During the crisis, the symptoms become more severe and spasms occur in the airways. This condition defined as an asthma attack leads a drowning sensation, requires immediate treatment.
Urticaria, which is characterized by itching and swelling of the skin, often develops in food and drug allergies and insect bites. However, parasitic diseases, thyroid diseases and some systemic diseases (rheumatic diseases, blood diseases, cancers, etc.) that may cause urticaria should also be investigated. Another allergic disease observed in the skin is eczema in which fluid-filled blisters occur. Itching is one of the typical complaints of eczema. Over time, skin flaking, thickening and shedding occur. The reason is mostly the materials that the skin comes into contact them such as clothing, jewellery and devices.
Atopic dermatitis is a skin disease that develops mostly in children. This disease also occurs for allergic reasons. Itching, dryness, tenderness, redness, flaking, bleeding and inflammation are the most characteristic features of certain areas of the skin (cheek, neck, elbow, knee). This disease has a close association with food allergies. Although it is difficult to treat, the severity of signs and symptoms decreases by revealing the triggering factors and taking precautions. Bathing with warm water, using natural soap, choosing cotton clothes, avoiding the sun and visiting a physician on time are some of these measures.
While food and drug allergies often cause different types of skin rashes, sometimes anaphylactic shock develops. Anaphylactic shock is also most frightening complication in bee allergy. Therefore, such serious allergies should be diagnosed and treated beforehand.
Diagnosis of Allergic Diseases
The diagnosis, in allergic diseases, is made by the patient's history, physical examination and some laboratory tests. Laboratory tests are mainly divided into two groups: the tests made on the patient are the first and blood tests are the second.
The tests made on the patient:
Skin tests
They are still the gold standard in the diagnosis of allergy. Standard test solutions prepared from the extracts from pollen (grass, grass, wood, cereals), mould, mite, animal skin rash, rubber, food and bee venom apply on the skin surface (Skin prick test) or under the skin (intradermal test). For this purpose, special needles are used which create a small scratch on the skin or allow the allergen to be delivered under the skin. Evaluation is performed 15 minutes after the allergen solutions are applied to the skin. The responsible allergen is determined according to the magnitude of the skin swelling.
These tests are also used in drug allergies. The main drugs investigated for this purpose are antibiotics (beta lactam), drugs used in local or general anaesthesia, muscle relaxants, narcotic painkillers, epilepsy drugs, chemotherapy drugs, substances used in radiological examinations and biological agents.
Patch test:
It is made by sticking the standard test material containing allergens to the back. The test material used for this purpose contains more than 20 allergens (perfumes, medicines, preservatives, antioxidants, sweeteners, cosmetics, plastics, adhesives, various chemicals, etc.). Evaluation is made 48-72 hours after this application. At the end of this time, the responsible allergen is determined according to the degree of skin rash, itching and watering.
Pulmonary function tests:
These tests are performed in patients who are thought to have allergic asthma. A device called as spirometry is used for this purpose. According to the results, the degree to which the respiratory tract and lung capacity are affected by the disease is revealed. This test is sometimes carried out after a while of administration of drugs (15-20 minutes or 15 days) that open the airways. Thus, it is evaluated whether the pulmonary functions improve with medication.
Provocation tests
It is done to determine whether an allergen cause the patient's complaints. It is often used to reveal respiratory sensitization or to identify the responsible allergen (medicine, food). For this purpose, the suspected allergen is administered by mouth, nose, eye or respiratory tract depending on the organ affected by the disease. It is a life-threatening method for the patient. For this reason, these tests are performed under the supervision of an expert and taken necessary measures for emergencies.
Blood tests:
These tests are designed to detect the allergen responsible for the disease. The basic principle here is to show antibodies that develop against the allergen in the blood. For this purpose, 3-5 millilitres of blood taken from the vein of the patients is enough.
Treatment
The first advice given to patients with allergies before starting treatment is to avoid the responsible allergen. Drug treatment comes later. The drugs and methods with different properties are used according to the affected organ and disease. These are tablets, sprays, drops and injections that are taken via mouth, nose, eyes, skin and respiratory tract. Such medications alleviate symptoms in the short term, while in the long term they may partially improve the symptoms.
Vaccine therapy called as immunotherapy is used in the patients whose complaints do not regress with conventional treatments. This method is the only treatment that can cure allergic diseases. For this purpose, standard allergen extracts are injected via subcutaneous route at certain intervals. The treatment is carried out in two stages as initial and maintenance treatment. In the initial treatment, increasing doses are administered at frequent intervals (1 injection per week), whereas in maintenance therapy a certain dose of allergen is administered at larger intervals. In conventional immunotherapy protocols, the treatment lasts 3-5 years. In recent years, shorter protocols have also been developed.
The most common side effects of vaccine treatment are itching and redness at the injection site. However life-threatening reactions (anaphylactic shock etc.) are also developed rarely. Therefore, patients should be observed for at least half an hour after vaccination.
Another method of immunotherapy is sublingual administration of allergens in the forms of drop or tablet. Although this method has become more widespread lately, it is not an alternative treatment instead of vaccine treatment yet.