Low Dose Computed Tomography
THE ROLE OF LOW DOSE LUNG COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER
Incidence and Etiology of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the most common in male population and second in female population among the cancer types which spreads fastly. Multipl personal and environmental factors effect the occurance of lung cancer. Among the environmental factors, smoking is the most important one whereas genetic predisposition is the first among the personal factors. Other environmental factors are; asbestos, benzene, crom, nickel, cadmium,vinyl chloride, arsenic and UV that are widely used in developing industry.
The Relationship Between Smoking and Lung Cancer
Smoking is the most important environmental factor of the lung cancer, and the relationship between smoking and lung cancer is known for almost 50-60 years. It is also proved that smoking causes many other cancer types. According to many medical researches, 85-90% of the lung cancer cases are related to smoking and smoking increases the lung cancer risk 5-15 times. The age of starting smoking, total time of smoking and the number of cigarettes smoked per day all affect the occurance of lung cancer. Early starting, smoking for a long time and too many cigarettes smoked per day increase the risk of lung cancer whereas giving up smoking decreases the risk.
Lung cancer is one of the progressive cancers among other cancer types. Unfortunately, with current medical facilities, patients with end-stage diseasecan not have good response to treatment. If patients are early diagnosed, he or she may have a chance for treatment. Thus, prevention such as stopping smoking or keeping away from places where others smoke, is more important Many countries have made legal restrictions about smoking and this law is currently applied.
There is also a correlation between lung cancer and passive smoking. It ’s known that the risk of developing lung cancer in passive smokers increases 2-5 times.
Importance of The Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
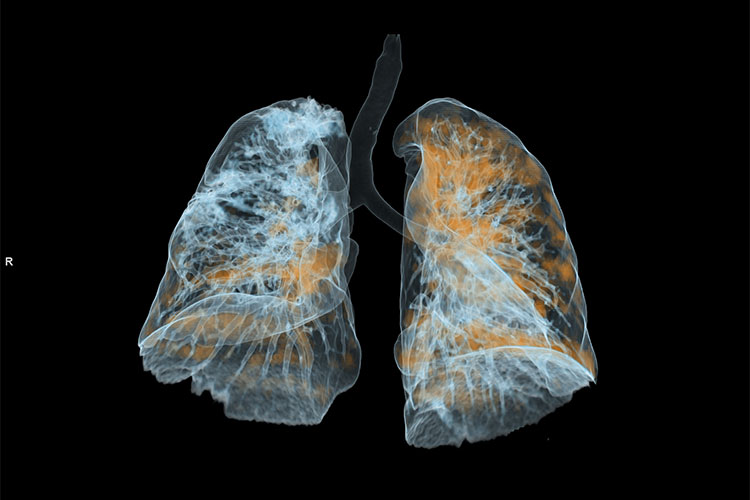
If lung cancer is early diagnosed, it can be treated. Early stage lung cancer can be asymptomatic, therefore imaging heavy smokers’ lungs may increase the chance of early diagnosis which leads to effective treatment. CT is a highly sensitive imaging technique which can show lung nodules and differenciate the benign lesions. However, high dose radiation is an important issue. In this context, cancer screening can be made with low dose radiation and good quality CT images with low dose lung CT. Currently, in most of the centers, this method is preferred for detection of lung cancer.
The Difference of Low Dose Computed Tomography
Low dose computed tomography technique involves lower radiation than normal computed tomography with obtaining adequate CT images. To establish cancer foci, technique should provide tissue contrast. With low dose CT, X-ray tube flow rate decreases 50 mAs (Originally 250 mAs), and this reduction does not disturb tissue contrast. The radiation exposure in normal thorax CT is 5mSV, whereas this value decreases to 1mSv in low-dose CT, which is a big difference.
This technique is available in Baskent University Medicine Faculty Department of Radiology.
A new and First application in Turkey at Baskent University: Dual-Energy CT Pulmonary Angiography imaging with ultra-reduced Contrast Media
Computed tomographic (CT) pulmonary angiography (CTPA) has now been widely accepted as the standard test for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary emboli. The application of CTPA is limited in patients with impaired renal function because of the risk of developing contrast medium–induced nephropathy. Many patients at risk for developing pulmonary embolism are elderly and have comorbid conditions that increase the risk for renal injury.
Dual-energy CT has recently been reported for use in CTPA and last studies have focused on testing the diagnostic accuracy of the perfusion map generated by using dual-energy CT.
The potential risk of contrast media (contrast material–induced nephrotoxicity), an acute decline in renal function following the administration of intravascular contrast material in the absence of other causes is thought to be a limitation of CTPA, particularly in patients with borderline renal function. Although recently it has been shown that the risk of nephrotoxicity with contrast-enhanced CT may be overstated. Low-tube-voltage scanning may facilitate contrast medium reduction used in new Dual-Energy CT systems (Siemens Somatom Force) by affording an increase in image signal intensity while maintaining compatible image quality, and effective radiation dose.
The significant reduction in iodine-contrast media with dual-energy CTPA protocol, which routinly preferred in our center has potential to offer the most important and direct benefit to patients in terms of renal protection.
DUAL ENERGY CT
Dual Source CT (DSCT) is equipped with two data measurement systems, each consisting of one X-ray tube and one corresponding detector. Two measurement systems are oriented in the gantry with an angular offset of 90 degrees offering a subset of unique advantages. In contrast, a conventional multislice CT uses only one single X-ray generator.
Generally, DSCT technology comprises two different operating modes: both X-ray tubes work at the same kV setting or every X-ray tube works at different kV and its ideal mA settings.
The two X-ray source/detector systems rotate simultaneously capturing image data in half the time required with conventional technology. With DSCT it is possible to double the temporal resolution to 83 ms compared with that of a single source CT, and increase the speed of acquisition while reducing the radiation dose significantly.
Dual energy means that the system uses two X-ray sources simultaneously at different energy levels to improve the energy separation, which is the key to high sensitivity and specificity in spectra imaging. This makes it possible to differentiate not only between fat, soft tissue and bone, but also between calcifications and contrast material on the basis of their unique energy dependant attenuation profiles. Furthermore, functional parameters such as iodine concentration in the lung, myocardium or tumors can be acquired.
 |
 |
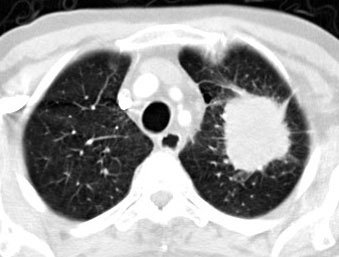 Düşük doz Bilgisayarlı Tomografide saptanan sol akciğer kanseri |










